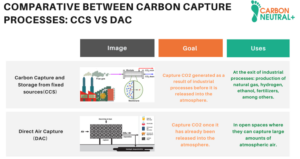
What is carbon capture?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions generated by human activities have led to an accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that is causing an increase in
If you are interested in reducing the environmental impact of your activities or those of your company, there are different methods you can implement. First, reducing your greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions is always the best place to start. You can do this by modifying or replacing activities or products with a lower carbon footprint. But there’s another way: carbon offsetting. This method allows you to reduce your environmental impact and even to completely neutralize your carbon emissions.
This article will tell you what carbon offsetting is and how you can do it for your activities or company. We will also talk about something fundamental: how to measure these emissions.
Always remember that the best way to offset your carbon footprint is to follow these steps: measure, reduce, and offset.
Carbon offsetting
Carbon offsetting or carbon footprint offsetting is the process of acquiring carbon credits (or other emission reduction certificates) to reduce an individual’s or organization’s total net emissions. In other words:
Net emissions = Emissions generated – Emissions offset
In summary, carbon offsetting reduces the net emissions of a company, individual, event, or product’s activities by effectively reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases (GHG) in the atmosphere. This reduction is achieved through projects certified to international standards. Offsets are measured in TN CO2eq (tons of carbon dioxide equivalent)
The role of carbon credits in offsetting carbon footprints
If we know the amount of emissions a specific activity generates, we can calculate the amount of CO2eq tons to offset. This carbon offsetting is achieved through certified carbon credits from one of the following projects:
The carbon credits associated with these projects account for 1 ton of CO2eq absorbed or prevented from being released into the atmosphere.
To give an example of each case:
Reforestation projects generate carbon credits for each ton of CO2eq they absorb from the atmosphere through their capture in tree biomass.
On the other hand, renewable energy projects avoid releasing CO2eq emissions into the atmosphere, reducing the demand for energy from fossil fuels by increasing the supply of renewable energy.
Therefore, if a company emits 10 TN CO2eq into the atmosphere, it needs 10 carbon offsets to neutralize its carbon emissions completely.
Why is carbon offsetting important?
As we mentioned above, the steps to reduce the environmental impact associated with our carbon footprint are as follows:
However, sometimes an internal carbon emissions reduction is not possible. For example, this happens with mandatory air travel or industrial processes for which no more sustainable option is available. In these cases, carbon offsetting is a viable alternative that effectively reduces the total impact of these activities and contributes to reducing the concentration of GHG in the Earth’s atmosphere.
How are GHG emissions measured?
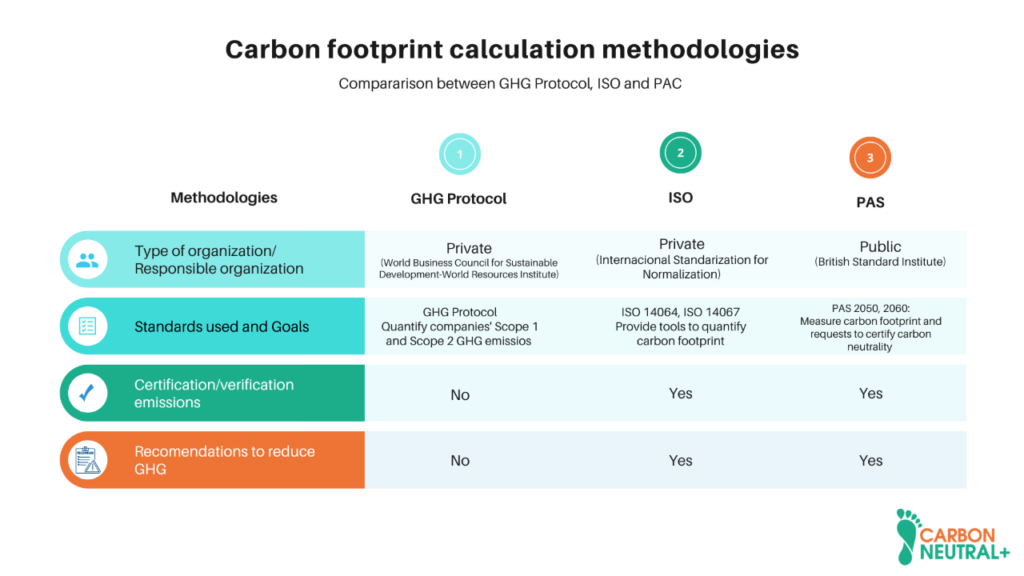
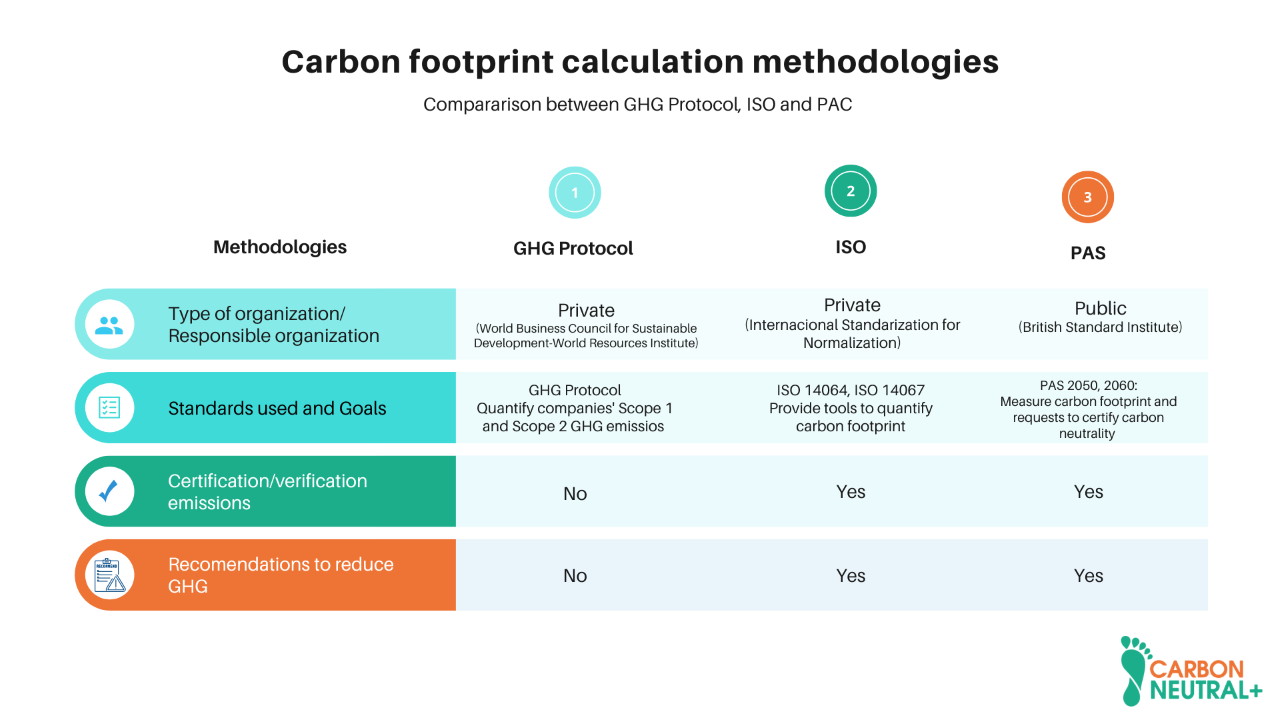
For a correct carbon offsetting, we need to quantify GHG emissions. To define how this measurement will be carried out, it is necessary to know the most essential points of the primary emission calculation standards. These will determine the methodology to be used to choose one or the other depending on the needs of the organization or the characteristics of the activities or products to be analyzed.
Specific standards analyze the GHG inventory at the organizational level: GHG Protocol, ISO 14064, and PAS 2050. On the other hand, the standard that analyzes only products and services is ISO 14067. The main characteristics of each of these standards will be described below.
Also, if you want to know the step-by-step to calculate your carbon emissions, you can read our article: What is carbon footprint and how to calculate it?
GHG Protocol
The Greenhouse Gas Protocol is one of the most widely used tools for calculating GHG emissions and preparing inventories. It was created from the union of several companies, non-governmental organizations, and other agents under the coordination of the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
This standard was created to avoid multiple GHG quantification initiatives and thus to provide consistency among the different mechanisms. It also allows cross-sectoral and sector-specific analyses, providing information on the sector’s activities and emission factors.
The GHG Protocol allows the calculation of scopes 1, 2, and 3, and has an implementation methodology based on the following points:
ISO 14064
ISO 14064 is an international standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and focuses on designing and developing the organization’s GHG inventory.
Its requirements can be simplified into three dimensions:
The standard is divided into three parts:
PAS 2050
PAC 2050 is another leading methodology for calculating the carbon footprint of organizations. Its initials, Public and Available Specification indicate its unrestricted access.
This specification establishes the requirements needed to perform a life cycle analysis of a product or service’s GHG emissions.
The methodology described by PAS 2050 has some basic principles to follow:
In this sense, the organization must ensure that the analysis of the life cycle of its products is complete. In turn, it distinguishes the implementation according to its applicability, i.e., whether it is a life cycle based on a product within B2B (Business to Business) or B2C (Business to Customer).
ISO/TS 14067
Finally, ISO 14067 details the principles and requirements for measuring the carbon footprint of products (including both products and services). Its goals are:
The following chart summarizes the mentioned standards for measuring and reporting GHG inventories.
And there is one other way to measure your GHG emissions: carbon footprint calculators.
A carbon footprint calculator is a tool for calculating the carbon emissions generated by an individual or company. This calculation allows us to know the exact amount of emissions to be offset and thus the carbon credits to be purchased.
In Carbon Neutral + we have a business carbon footprint calculator with which you can quantify the carbon emissions of your company. Access our calculator through this link.
How to buy carbon credits to offset your emissions?
At CARBON NEUTRAL+ we support different carbon offset projects by offering BIOCARBON+. This is an ecolabel that allows companies to offset their corporate carbon footprint through carbon credits certified by the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS). And, at the same time, to have a positive local impact since 1/3 of the funds are destined to finance reforestation projects in Argentina with local NGOs.
If you want to offset your company’s emissions by purchasing carbon credits backed by these projects, you can enter our MARKETPLACE.
Conclusion
Carbon offsetting is a climate change mitigation strategy that reduces the concentration of GHGs in the atmosphere. Therefore, carbon footprint offsetting is a crucial concept that helps us reduce the environmental impact of GHG emissions generated by our individual activities or in the processes associated with our company.
It is important to remember that it is always important first to try to reduce your carbon footprint. To do this, it is first necessary to measure it. Different measurement standards, such as the GHG protocol, establish guidelines for measuring, communicating, and developing GHG emissions inventories.

Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions generated by human activities have led to an accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that is causing an increase in
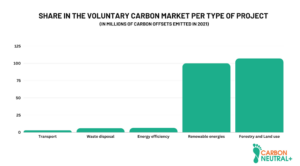
According to the Emissions Gap Report 2022, the growth rate of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions has declined over the last decade. Between 2010 and
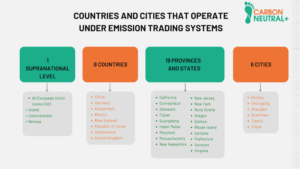
As international agreements related to corporate greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) come into force, the regulations associated with the generation of these emissions increase. This is
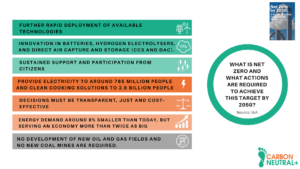
Climate change is one of the greatest concerns of our time. This phenomenon is generating consequences that are difficult to reverse, such as an increase

The Paris Agreement is an international agreement adopted on December 12, 2015 during the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP21) in Paris, France. One of

As the world faces the looming effects of climate change, more and more companies are recognizing the importance of adopting sustainable strategies that aim to
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |