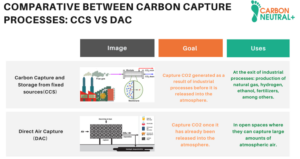
What is carbon capture?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions generated by human activities have led to an accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that is causing an increase in

Carbon credits are a method used to offset carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, allowing both companies and individuals to reduce their carbon footprint.
Any individual can purchase carbon credits, but these are generally purchased by companies. This purchase is made with the aim of offsetting the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions generated by the company due to, for example, its industrial processes.
Due to the popularity they have gained in recent years, there are many ways to generate carbon credits. Also, the secure purchase of these credits is also becoming easier and easier.
But,
In this article we will answer all these questions, but stay until the end and we will also tell you a very simple and easy way you can use to securely buy carbon credits.
What are carbon credits?
Carbon credits (also called carbon offsets) are a climate change-mitigation mechanism initially proposed in the Kyoto Protocol in 1997. They represent the removal of one tonne of carbon dioxide (tnCO2eq) from the Earth’s atmosphere.
Carbon offset projects capture or prevent greenhouse gases (GHGs) from being emitted into the atmosphere. This way, they aim to contribute to mitigating the causes of climate change.
These credits are issued by different organizations that contribute to the removal of these GHGs through different carbon credit projects.
Who verifies the authenticity of carbon credits in the market?
To guarantee their veracity, carbon credits projects are verified by international entities that validate and certify the reduction of emissions from the project and its socio-environmental benefits.
In order to certify under one of these entities, the company issuing these carbon credits has to comply with a strict set of standards. Once the company has gone through the entire verification process, it is awarded a certification and the logo of the regulatory entity.
This certification provides buyers with the assurance that the company issuing the credits has undergone auditing processes that ensure the traceability of all its processes.
These certification entities represent the voluntary market for carbon credits, and some examples are:
You can learn more about the most widely used carbon credit standards in this article of our blog.
What does a carbon credit represent?
Carbon credits represent that one ton of carbon dioxide equivalent (tn CO2eq) was absorbed or prevented from being released into the atmosphere.
That is, they can either capture 1 tn tnCO2eq from the atmosphere or prevent 1 tnCO2eq from being released.
For example:
What does it mean to be a carbon neutral company?
Companies usually purchase carbon credits in order to offset the carbon emissions associated with their productive processes.
A carbon neutral company has a net zero emissions balance. In other words, it emits the same amount of GHGs as it offsets.
As can be seen in our article How to become a carbon neutral company, the path towards such neutrality consists of 3 steps:
1- Measure: the company must quantify its CO2eq emissions.
2- Reduce: the company takes action to reduce as much of its CO2eq emissions as it possibly can.
3- Compensate: finally, the company can compensate for the emissions it couldn’t reduce in previous instances.
The last of these steps (compensation) must be carried out through the mechanism of purchasing carbon credits.
What are the benefits of purchasing carbon credits?
Some of the benefits of purchasing carbon credits are:
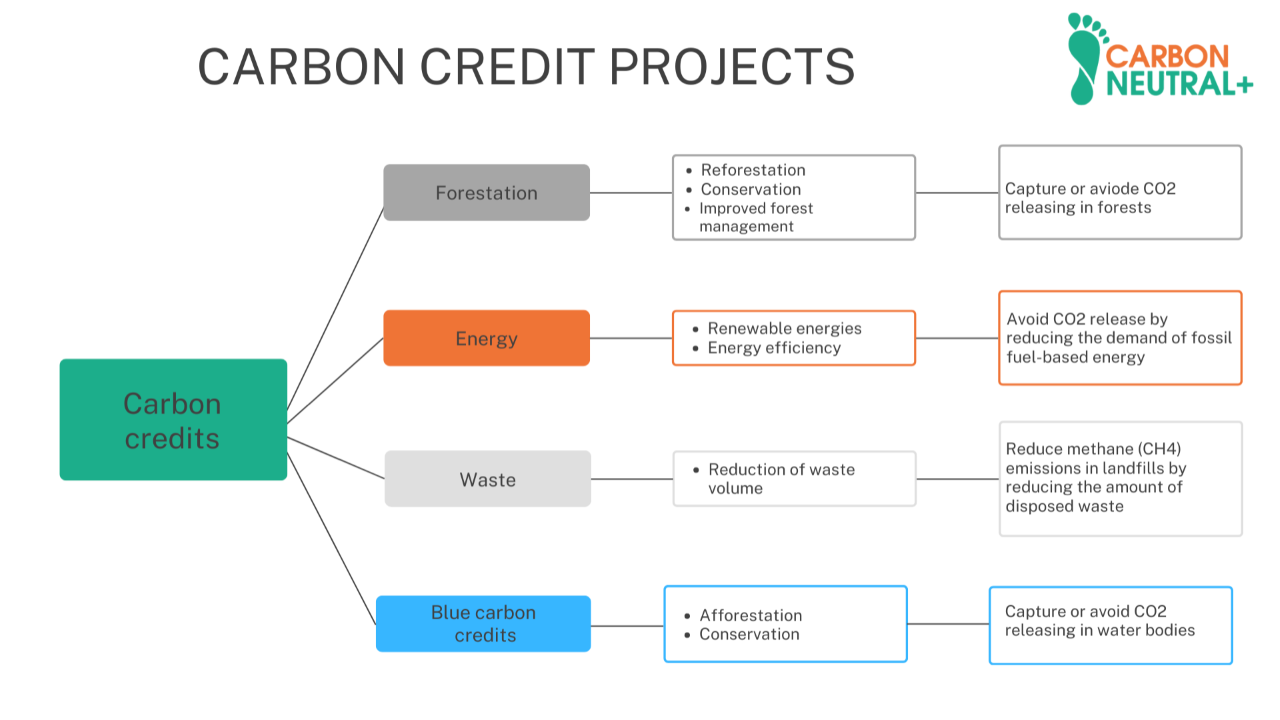
What types of projects emit carbon credits?
Afforestation projects
Forests are composed of trees that naturally extract CO2 from the atmosphere and store it in their biomass (wood, leaves and roots). Currently, they are one of the most cost-effective and scalable opportunities for sequestering carbon.
By recognizing the importance of forests as carbon sinks, people around the world are starting to create more and more projects to protect and restore these ecosystems.
There are three types of carbon credit generating projects linked to afforestation:
Reforestation
These projects are linked to the planting of new trees. Reforestation projects plant thousands of trees, often transforming degraded lands into forests.
Reforestation projects generate carbon credits for each ton of CO2 they remove from the atmosphere through their capture in the tree’s biomass.
Conservation
Conservation projects protect forests to prevent their deforestation. Forest conservation aims to protect the enormous carbon stored in existing forests.
Forests not only store carbon in their leaves, branches and roots, but also in their soils. Therefore, when an ecosystem is deforested, both the carbon stored in the biomass and the carbon that has been stored in the soils over the years is released.
In these projects, carbon is not sequestered, but rather carbon stored in the biomass of the forest ecosystem is prevented from being released.
Improved forest management
These projects seek to improve the carbon storage potential of forests. Improved forest management projects protect natural habitats and allow for sustainable wood harvesting.
Carbon credits are generated by improving the carbon storage potential of forests compared to that achieved with typical forestry practices.
Energy projects
Renewable energy projects
Renewable energy projects include the production of hydroelectric, wind, solar, biomass and other renewable energies.
These projects are crucial as climate change mitigation strategies because they cooperate in the energy transition to clean and renewable energies.
Renewable energy projects lead to so-called “indirect emission reductions”. In other words, emissions are not reduced in situ where the project is developed, but at the thermoelectric power plant that has to produce less fossil fuel-based energy due to the increased supply of renewable sources.
Energy efficiency projects
Efficient products or systems use less energy than conventional technologies used to perform the same task. Most energy efficiency offset projects are implemented in large industrial facilities.
Like renewable energy projects, they also produce indirect emission reductions. In other words, emissions are not reduced in the building where the efficiency improvements are implemented, but in the power plant which has to produce less electricity due to reduced energy demand.
Waste treatment projects
Organic matter decomposition in landfills produces GHGs, such as methane (CH4), which has a global warming potential 25 times greater than carbon dioxide.
Here, carbon credits are generated by reducing CH4 emissions by reducing the volume of waste that ends up in landfills. Instead, they are processed into usable products such as compost or biogas.
Blue carbon credits
Blue carbon credits seek to promote the conservation and restoration of natural blue carbon sinks. They aim to capture atmospheric CO2 or prevent the release of carbon stored in marine soils.
To learn more about blue carbon credits, you can read our article: Blue carbon credits Blue carbon credits: What are they and what is their importance?
The following image summarizes all the types of carbon credits mentioned:
How to buy carbon credits?
At CARBON NEUTRAL+ we support different carbon offset projects by offering BIOCARBON+. This is an ecolabel that allows companies to offset their corporate carbon footprint through carbon credits certified by the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) and, at the same time, have a positive local impact since 1/3 of the funds are destined to finance reforestation projects in Argentina together with local NGOs.
If you want to offset your company’s emissions through the purchase of carbon credits backed by these projects, you can enter our MARKETPLACE.
Conclusion
In summary, carbon credits are a tool that allows companies to demonstrate their environmental commitments by reducing their carbon footprint.
Currently there are different types of carbon offset projects and these can be purchased very easily through intermediaries, such as CARBON NEUTRAL +.

Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions generated by human activities have led to an accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that is causing an increase in
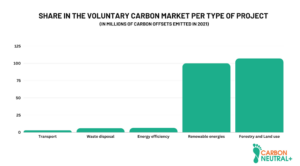
According to the Emissions Gap Report 2022, the growth rate of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions has declined over the last decade. Between 2010 and
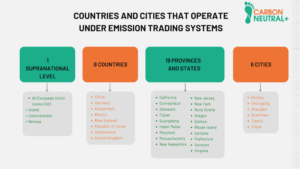
As international agreements related to corporate greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) come into force, the regulations associated with the generation of these emissions increase. This is
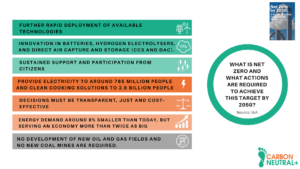
Climate change is one of the greatest concerns of our time. This phenomenon is generating consequences that are difficult to reverse, such as an increase

The Paris Agreement is an international agreement adopted on December 12, 2015 during the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP21) in Paris, France. One of

As the world faces the looming effects of climate change, more and more companies are recognizing the importance of adopting sustainable strategies that aim to
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |